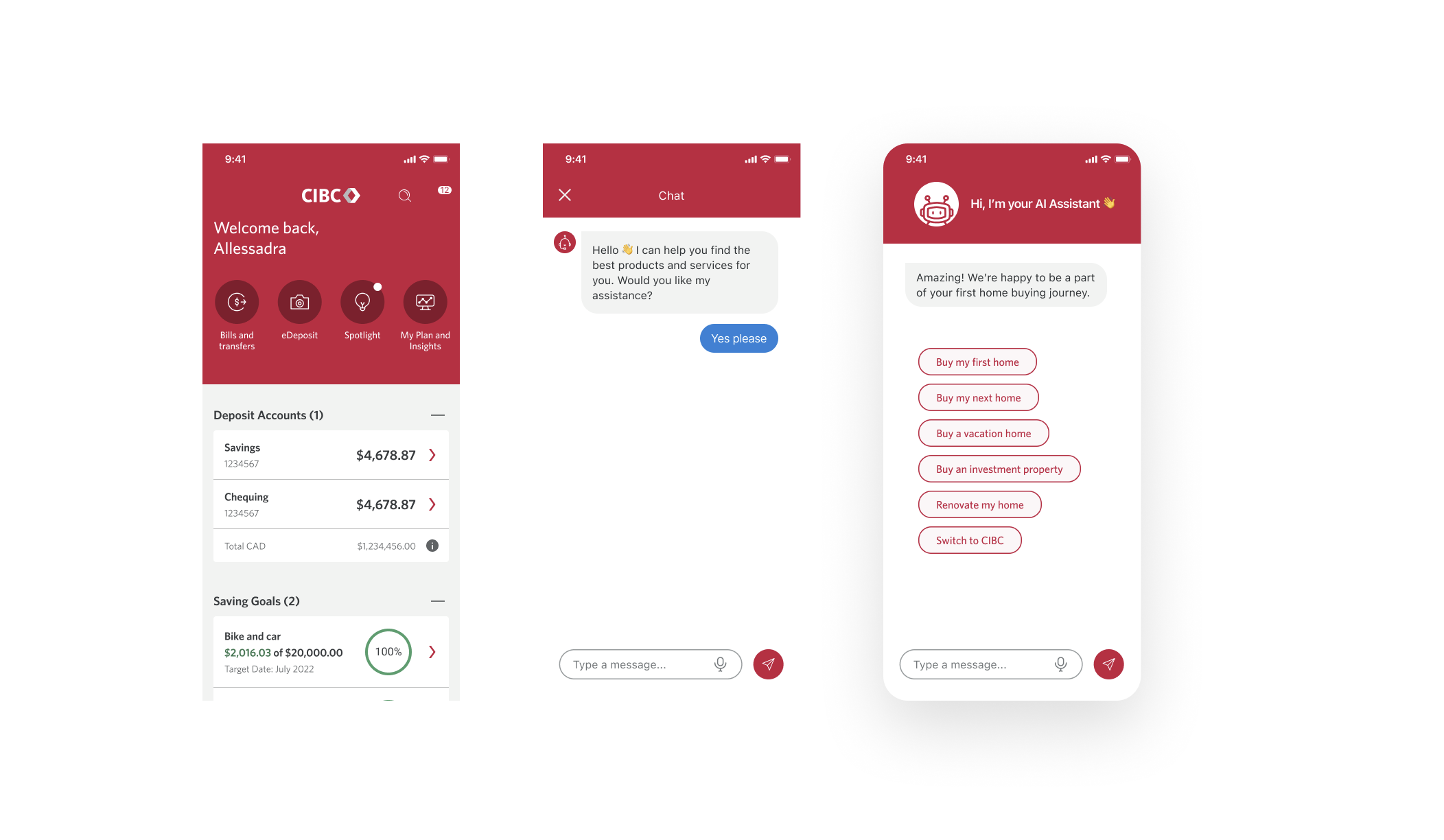
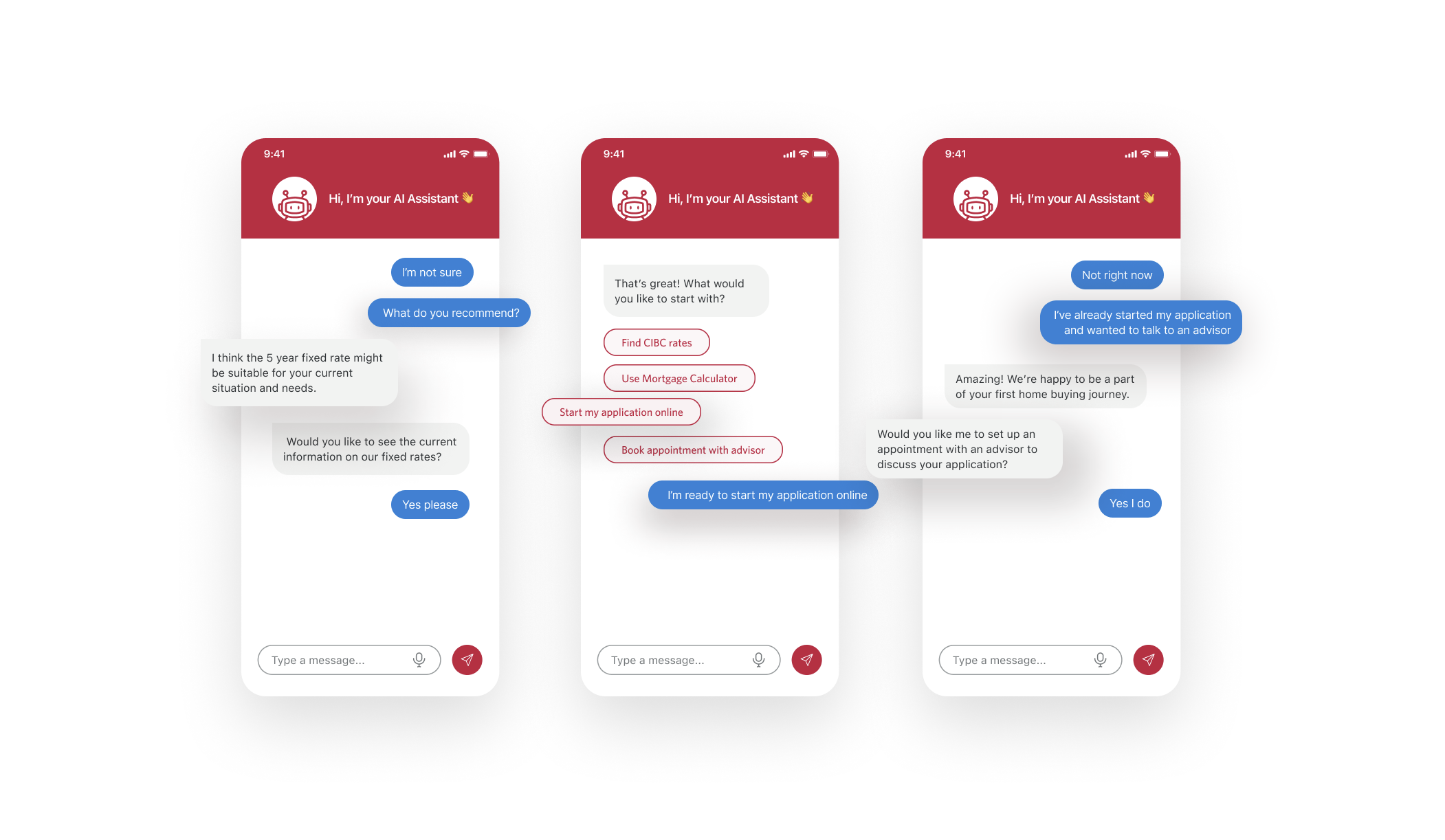
Chatbot
Evolving Chat/AI trends have changed the way banks show up for their clients.
Project Goal
-
SBU Workshops to uncover use cases, current solutions and pain points
Interviews with LOB partners (chatbot POs) to understands potentials areas of improvements
User interviews for internal chatbot users
synthesized arch integration diagrams with the selected vendors
Market research for UX best practices for Chatbots
Design recommendations to better chatbot use
Competitor research on capabilities and solutions that provide good experience
-
Architecture and Technology diagram (data flow, data pipeline, tech components)
capability matrix for vendor comparison
Chatbot Training
Current vendor capability map
Dashboard & Reporting capabilities
Chatbot programming
Will vendor solutions work with our current tech stack
-
A well-researched and articulated POV on the current and future state of chat bots; including the following considerations
Features and Capability Map
KPIs & Data Metrics
Providing the landscape of the chatbots stakeholders at the bank and bridging gaps to reduce silos
Chatbot management and maintenance practices
Current cost and saving for different Chatbots
Chatbot use cases
Provide a clear understanding of CIBC’s current chatbot solutions, including chatbot capabilities, technology and pain points.
Design and demonstrate art of the possible enterprise solution for CIBC
Primary Research
- Common frustrations
Chatbot doesn’t understand the questions or has very limited access to answers (data). This makes for a terrible bot experience for users. Make sure to set up your bot in a way that it can answer questions.
- Common frustrations
Your chatbot has no personality – it answers dully and inflexibly like a machine. That’s neither the best customer experience nor the best impression for your brand.
- Common frustrations
There is no handover protocol. For some apps, like WhatsApp, it’s required to have a handover procedure from bot to human agent. However, it always makes sense to set up a handover process that leads customers to human agents that can help them tackle more complex issues.
- Common frustrations
The dialogue only follows rigid patterns, but cannot do anything with differently asked questions or comments, and is then stuck in an endless loop. Find happy flows that will smoothly allow your bot to ask for more information in different ways.
UX Best Practices
AI - Capabilities that are Required
Sentiment analysis
Determining the sentiment behind a phrase
Summarization
Expressing the most important facts of a text
Semantic search
Applying user intent the meaning to find the right content
Question answering
Answer questions posed in a natural language
Speech recognition
IA machine is able to process speech audio
Machine translation
The translation of one language to another by a machine
Insights
According to our research, companies that offer the greatest chatbot experiences have the following characteristics that set them apart from the competition: they are simple to use and navigate, with obvious clickable buttons. An interactive experience is crucial for keeping users engaged, which benefits the organization. Having the ability to comprehend various language structures, detect information while being capable of analyzing duplicates and other user expressions, and provide users with findings that are both particular and logical.
Frustrations
When the chatbot can't comprehend what the user wants or is attempting to say, the user becomes frustrated by the time it gets to the agent. It can be annoying for the user when they have to keep looping in order to reach a human agent and frequently the chat system shuts down in the process. Becoming stuck in an unending cycle while speaking to a dull robot.
Good user experience for the chatbot
Focusing on providing the client with their best experience in terms of navigating to the chatbot and engaging the chatbot - this in turn benefits in retaining users in a way that they would want to return.
Users don't enjoy the chatbot's ability to anticipate their wants by using a combination of wait time in answering the user, open-ended words and button interactions that lead to different pages and websites. hence decreasing the need for it and making the user's engagement with the AI feel human.
How can chatbots be implemented well?
Instead of diverting them to human agents, uncover genuine value for the user by using them to fill in the gaps left by the user.
To leverage the demands of the business, chatbots must be employed in a certain way. Successful chatbot implementations are correlated with using chatbots to transform business use cases rather than using chatbots to just utilize AI in general.
What clients require and how we can provide those needs should be the main points of focus.
If a consumer has a problem, they will call customer support. If they are in a place on an app or website where they need to contact customer support and the majority of problems are encountered, implement chatbots to make it seamless so they won't need to be frustrated when they meet the customer care representative providing contextual help: Instead of limiting a user's ability to contact customer service, chatbots could offer the needs.
LoBs In Focus
-
Currently have a chatbot powered by 24/7 AI
Current chatbot is not a good experience and isn’t bringing enough value
This could potentially be a high-value use case for implementing a better chatbot/scaling Watson
-
In 2021, there was a proposal (done by IBM) for a chatbot for Contact Centre employees for mortgages. Not Approved.
NSL chatbot work could potentially be leveraged
There’s an opportunity for client-facing chatbots since there’s no way for clients to access help outside of business hours
-
Knowledge Central is a Sharepoint site where contact centre employees get quick answers to serve clients
Mark Parker is working on NSL chatbot for KC
While smart search has improved the experience, there’s an opportunity for integrating a chatbot